
Loan Restructuring & Interest Recalculation Engine
The current spreadsheet-based process causes high error rates, customer disputes, and compliance risks due to limitations of the existing Loan Management System. The new solution operates alongside the LMS, supports all restructuring scenarios, ensures auditability and handles multiple changes per loan.
Date
October 2024
Industry
Banking
Role
Junior Business Analyst
Client
National Commercial Bank
The Challenge
National Commercial Bank manages a large retail loan portfolio using a legacy Loan Management System that assumes fixed interest rates and repayment schedules throughout a loan’s lifecycle. As customer financial hardship increases, the bank offers multiple loan restructuring options such as interest rate changes, maturity extensions, and payment holidays but these cannot be supported by the existing LMS. As a result, restructurings are handled manually by credit officers using spreadsheets, leading to significant calculation inconsistencies, a 12–15% error rate, frequent customer disputes, and revenue loss.
The Solution
The proposed solution introduces an Interest Recalculation Engine that operates alongside the existing Loan Management System without requiring any changes to the core platform. The engine automates all interest recalculations for restructured loans and supports all restructuring scenarios, including retroactive changes and multiple restructurings on a single loan, while preserving full payment history. It integrates with the LMS through batch processing, generates revised repayment schedules, posts adjustment transactions back to the LMS, and maintains a complete tamper evident audit trail to ensure regulatory compliance.
1. Problem Definition and Current State Assessment
1.1 Business Context
National Commercial Bank manages a retail loan portfolio of approximately 450,000 active loans with a total outstanding balance of $8.2 billion. The portfolio includes personal loans, auto loans, home improvement loans, and small business loans. The bank relies on a legacy Loan Management System (LMS) that has been operational for over 15 years and was designed under the assumption that loan terms remain fixed from disbursement to closure. As a result, the system does not natively support dynamic changes to loan terms during the loan lifecycle.
1.2 Restructuring Types Offered
The bank offers several loan restructuring options to support customers facing financial hardship. These include interest rate changes, which involve reducing or modifying the interest rate for the remaining loan term, typically used in cases of temporary income reduction or competitive rate matching. Another option is maturity extension, where the loan term is extended to lower monthly installments for customers unable to meet current payment obligations. The bank also provides payment holidays, allowing temporary suspension of payments for one to six months in situations such as job loss, medical emergencies, or natural disasters. In more severe cases, a combined restructuring approach may be applied, involving multiple restructuring types simultaneously.
1.3 Current Challenges
1.3.1 Calculation Inconsistencies
Loan restructuring calculations are currently performed manually by credit officers using spreadsheet-based tools. Different officers use different spreadsheet templates and calculation approaches, leading to inconsistent results. Interest calculations during payment holidays are interpreted differently across individuals, and partial payments made prior to restructuring are prorated inconsistently. Internal audit findings indicate that manual calculation error rates range between 12% and 15%.
1.3.2 Customer Disputes
Calculation inconsistencies have resulted in a high volume of customer disputes. On average, the bank receives approximately 180 disputes per month related to restructured loan calculations. Around 35% of these disputes lead to financial adjustments, resulting in revenue loss. The average dispute resolution time is 14 business days, and customer satisfaction for restructured loans currently stands at 2.8 out of 5.0.
1.3.3 Regulatory Compliance Risks
Regulatory authorities require a complete and transparent audit trail for all interest calculations related to restructured loans. The current spreadsheet-based process does not adequately document calculation logic, assumptions, or intermediate steps. A recent regulatory examination highlighted documentation deficiencies, exposing the bank to potential penalties estimated between $2 million and $5 million.
1.3.4 Operational Inefficiency
The restructuring process is highly time-consuming and inefficient. Each restructuring request takes an average of 4.5 hours to process, with credit officers spending nearly 60% of their time on calculations rather than customer assessment. The bank currently has a backlog of approximately 2,400 pending requests, resulting in an average wait time of 18 days. During peak periods, overtime costs reach approximately $85,000 per month.
1.4 System Constraints
The existing Loan Management System imposes several architectural constraints. It assumes a single fixed interest rate throughout the loan lifecycle and cannot store multiple interest rate periods. Repayment schedules generated at disbursement cannot be modified, and interest is calculated solely based on the original schedule. The system does not support retroactive changes, requiring all adjustments to be forward-dated. Additionally, while transactions are logged, calculation logic and intermediate steps are not captured, limiting auditability. Integration is restricted to batch-based file communication, as real-time APIs are not available.
2. Stakeholder Analysis
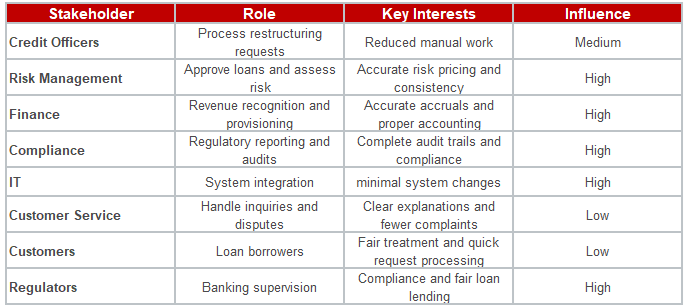
2.1 Stakeholder Identification
A comprehensive stakeholder analysis has been conducted to identify all parties with interest or influence in the Loan Restructuring & Interest Recalculation Engine initiative.
3. Current State Analysis
3.1 Current Situation
The current loan restructuring process operates through a fragmented, highly manual workflow spanning multiple disconnected systems and tools. The process was originally designed when restructuring requests were infrequent and loan terms were assumed to remain static throughout the loan lifecycle. As restructuring volumes and complexity have increased, these architectural assumptions have resulted in operational inefficiencies, inconsistent outcomes, and elevated regulatory risk. Each restructuring request requires significant manual effort and may take between several days and multiple weeks to complete, depending on approval queues and complexity.
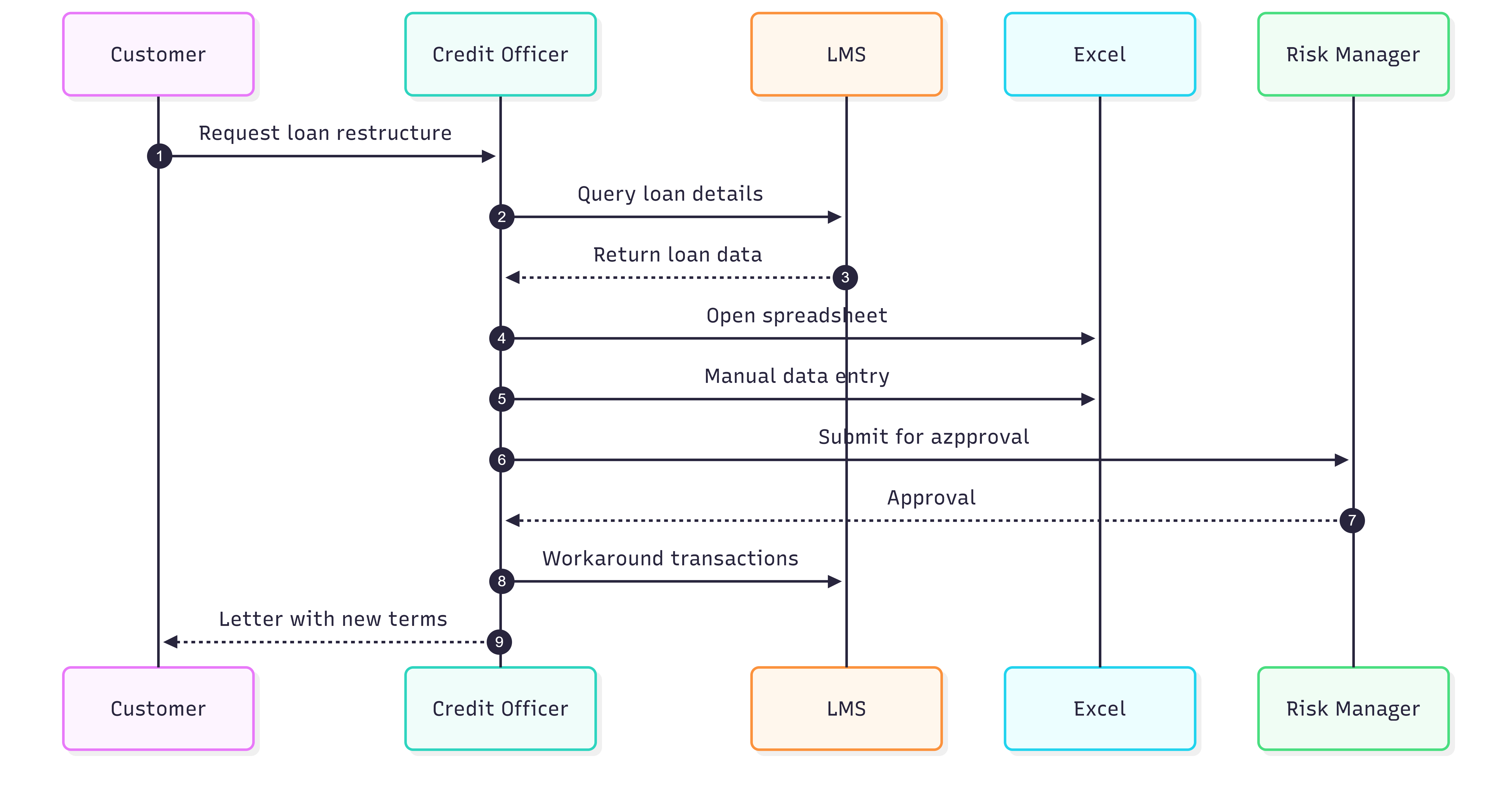
3.2 Current Restructuring Process
The current process starts with the customer contacting the bank to request a loan restructuring. A credit officer is assigned to evaluate the request and gather necessary documentation. The officer then manually analyzes the customer's financial situation, using various spreadsheet templates to model different restructuring scenarios. Once a preferred restructuring option is identified, the officer calculates revised interest amounts and repayment schedules using manual formulas within the spreadsheets. After internal approvals are obtained, the officer communicates the new terms to the customer and updates the Loan Management System with adjustment transactions. Finally, all documentation and calculations are archived for audit purposes.
4. Proposed Solution
4.1 Solution Overview
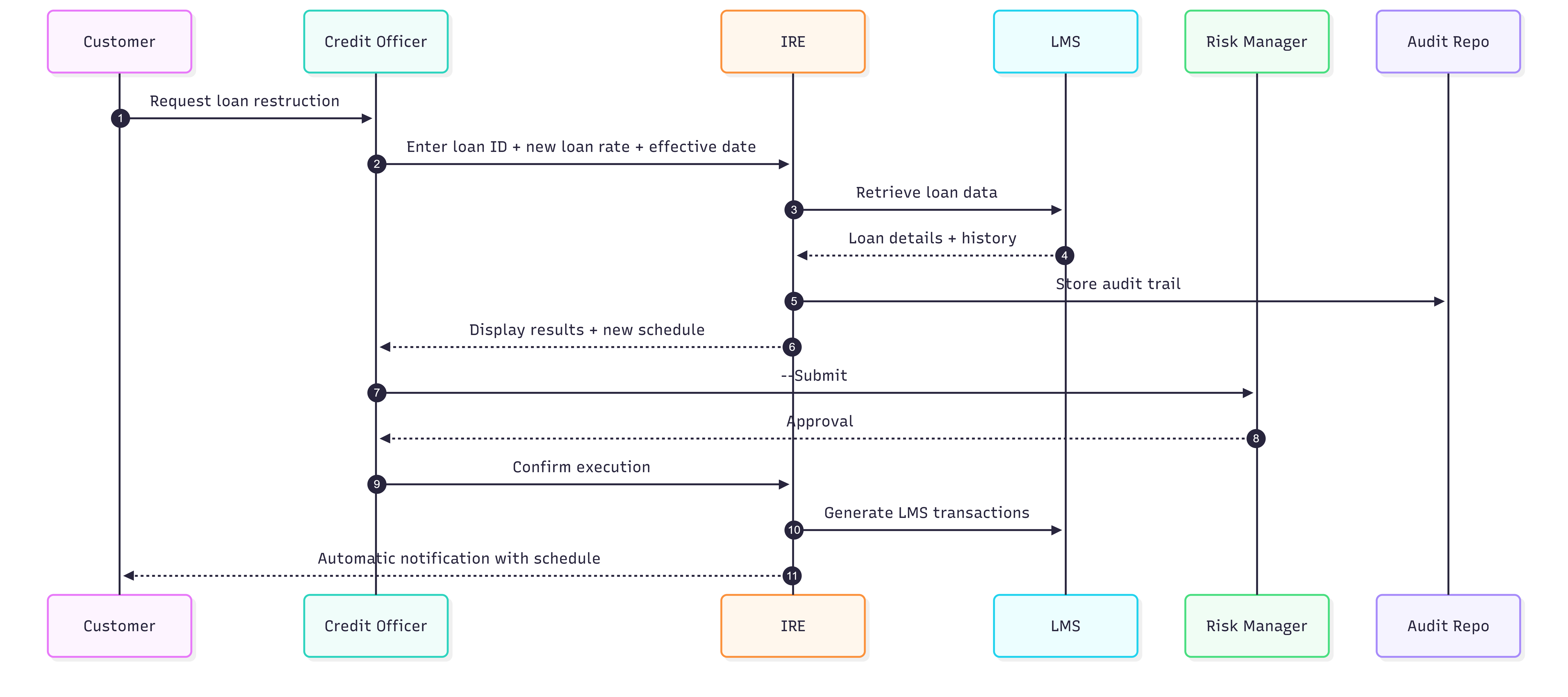
The proposed solution introduces an Interest Recalculation Engine (IRE) that operates as a complementary system alongside the existing Loan Management System. The IRE is designed to fully automate loan restructuring calculations while preserving the LMS as the authoritative system of record for loan data and transactions. By externalizing complex recalculation logic from the legacy system, the solution eliminates manual spreadsheet-based processing, significantly reduces error rates, and shortens restructuring turnaround time from several hours to under 30 minutes per request. Comprehensive audit trail capabilities ensure regulatory compliance by capturing all calculation inputs, decision logic, and outputs in a traceable and immutable manner.
4.2 Solution Architecture
The Interest Recalculation Engine is composed of modular components that collectively support accurate recalculation, schedule generation, auditability, and system synchronization. A dedicated integration layer retrieves loan data from the LMS and transforms it into a standardized format for processing. A centralized calculation engine applies consistent, policy-driven rules to support all restructuring scenarios, including rate changes, maturity extensions, payment holidays, and their combinations. Generated outputs are converted into revised amortization schedules and synchronized back to the LMS using controlled adjustment transactions, ensuring alignment between systems without altering legacy system behavior.
4.3 Key Capabilities and Benefits
The solution addresses critical business and regulatory challenges by standardizing interest calculation logic, supporting complex scenarios such as partial payments, retroactive effective dates, and multiple sequential restructurings, and providing full calculation transparency. A centralized audit repository preserves complete calculation histories and decision context, enabling efficient regulatory examinations and dispute resolution. Continuous reconciliation mechanisms ensure data consistency between the Interest Recalculation Engine and the Loan Management System. Overall, the solution improves operational efficiency, enhances customer trust through consistent outcomes, and significantly reduces compliance and financial risk.
5. Requirements of the Interest Recalculation Engine
5.1 Definition
This section defines the functional and non-functional requirements for the Interest Recalculation Engine (IRE). The requirements have been elicited through stakeholder interviews with credit officers, risk management, and compliance teams, assessment of existing Loan Management System capabilities and constraints, and alignment with regulatory compliance standards and operational efficiency objectives. Each requirement is assigned a unique identifier to ensure end to end traceability throughout the project lifecycle.
5.2 Functional Requirements
Functional requirements define what the Interest Recalculation Engine must do to support loan restructuring operations. These requirements describe the core system capabilities, data processing rules, and business logic needed to automate interest recalculation while ensuring regulatory compliance, calculation accuracy, and data integrity.

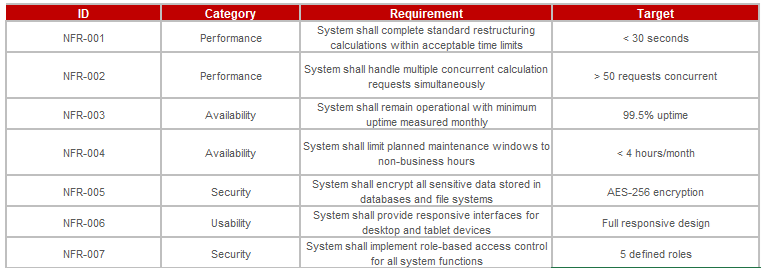
5.3 Non-Functional Requirements
Non functional requirements describe how the Loan Restructuring and Interest Recalculation Engine must perform in production by defining measurable quality attributes and operational constraints rather than specific features. For this initiative, they ensure the engine can process restructuring requests within the required turnaround targets, protect sensitive customer and loan information, and generate tamper evident audit records that meet regulatory expectations. They also cover reliability and consistency, including strong availability during peak volumes, the ability to scale for demand spikes and backlog reduction, and maintainability so calculation rules, day count conventions, and policy parameters can be updated safely with version control and full traceability. Together, these requirements set the performance, security, auditability, and resilience standards needed for stable and compliant end-to-end loan restructuring operations.
6. Conclusion
The analysis confirms that the current manual approach to loan restructuring and interest recalculation creates substantial operational inefficiencies, financial losses, and regulatory risk. Fragmented workflows, spreadsheet based calculations, and limited audit visibility lead to high error rates, frequent customer disputes, and increased compliance exposure, while Credit Officers spend most of their effort on manual calculations instead of customer assessment. The proposed Interest Recalculation Engine resolves these challenges by automating all calculation activities while retaining the existing Loan Management System as the authoritative system of record. The solution standardizes calculation logic, reduces processing time from hours to minutes, improves accuracy to near zero error levels, and introduces comprehensive audit capabilities that enable full traceability of every restructuring decision. By implementing this solution, the organization is expected to achieve significant reductions in processing time, customer disputes, and revenue leakage, alongside measurable improvements in customer satisfaction and staff productivity. More importantly, the Interest Recalculation Engine establishes a scalable, governed, and compliant foundation that transforms loan restructuring from a high risk manual process into a reliable and strategically valuable capability for the bank.
Outcomes & Impact
- Automated loan restructuring interest recalculation across all restructuring scenarios including rate changes, maturity extensions, and payment holidays
- Reduced restructuring processing time from approximately 4.5 hours to under 30 minutes per request
- Established a fully auditable and regulatory compliant calculation framework with complete traceability of inputs and outputs
- Improved customer satisfaction by delivering faster turnaround times and consistent, transparent restructuring outcomes